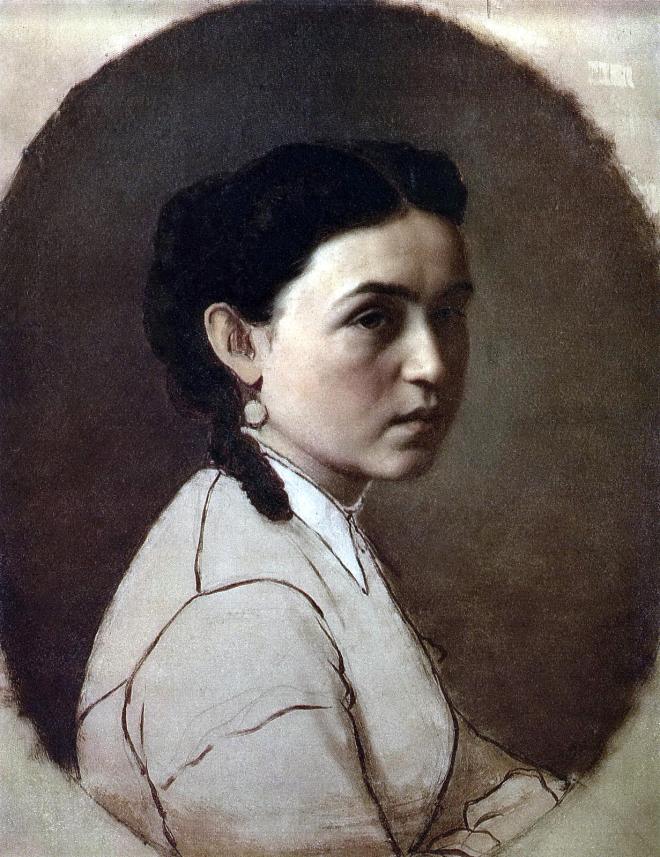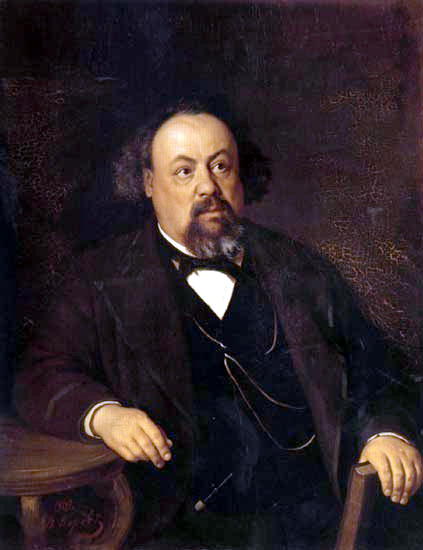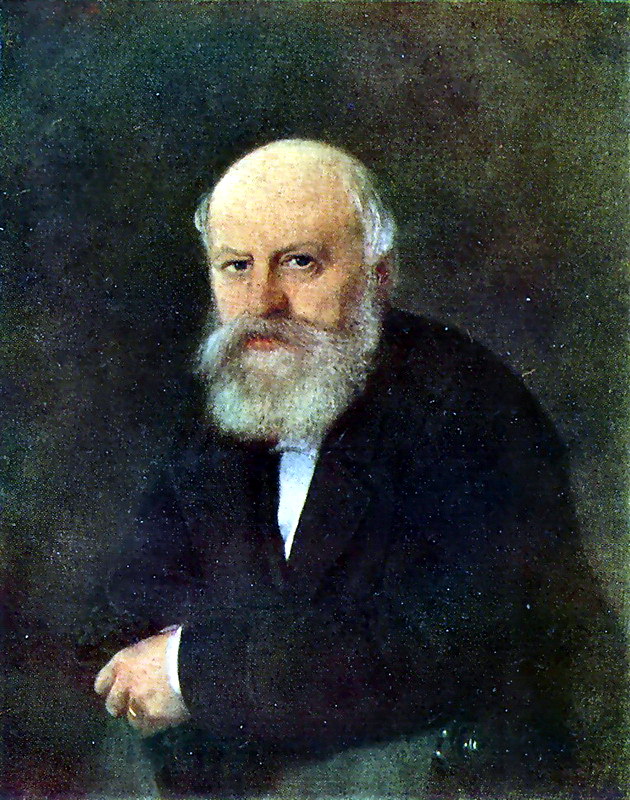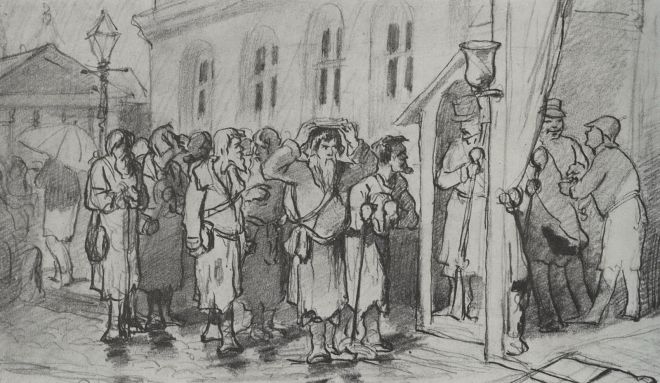| Livres bilingues | Read in English | Contact us Nous contacter |
| Littérature américaine | Littérature française | Littérature russe |
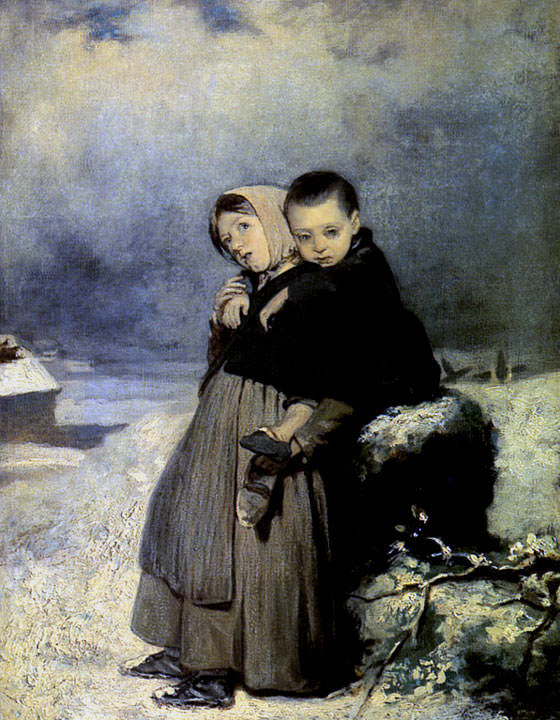
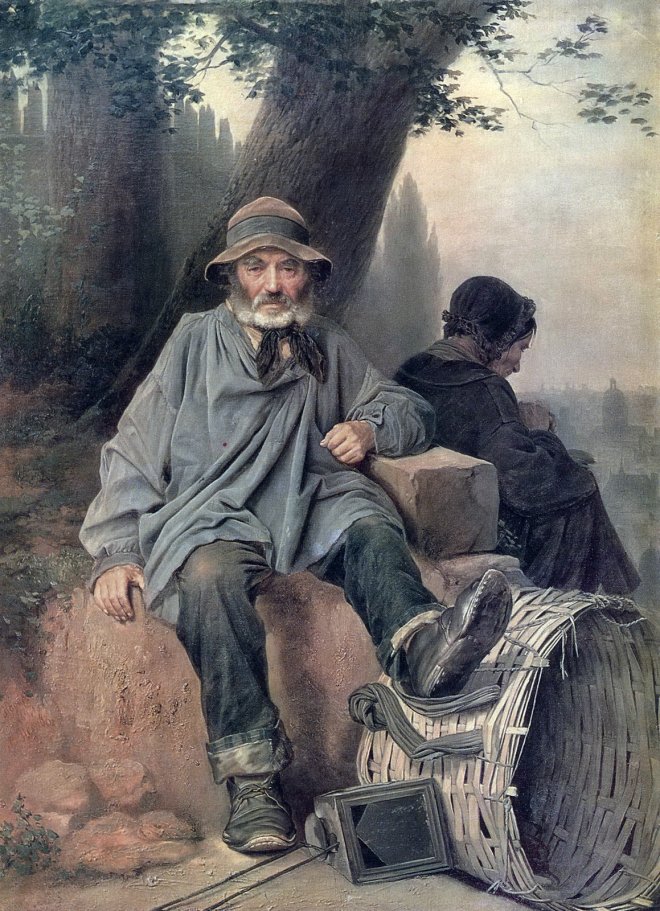
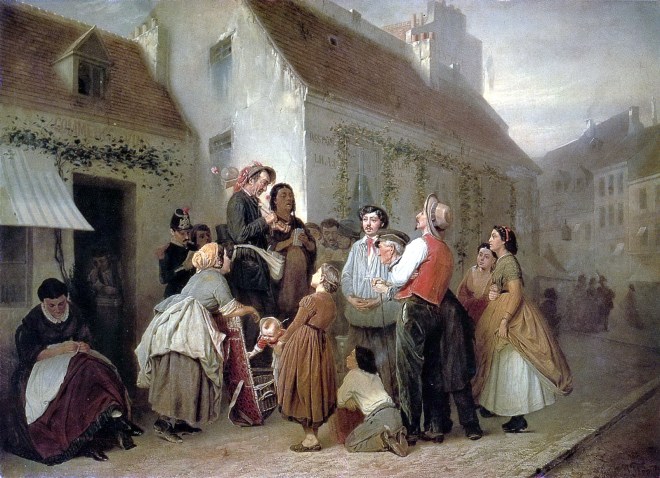
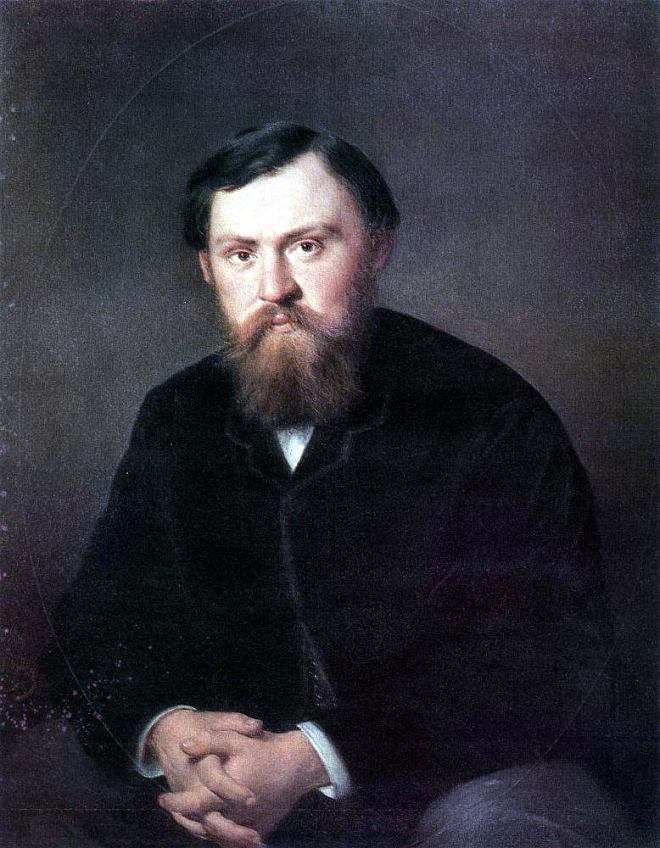
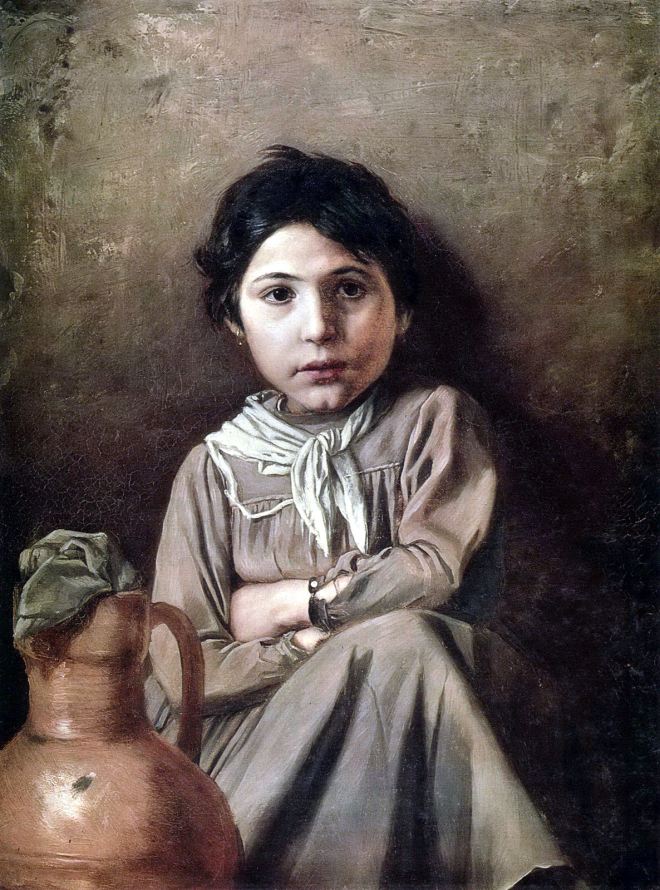
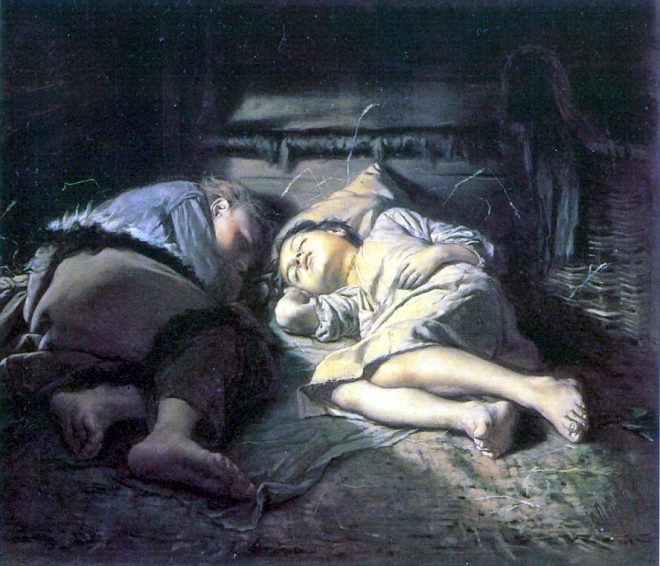
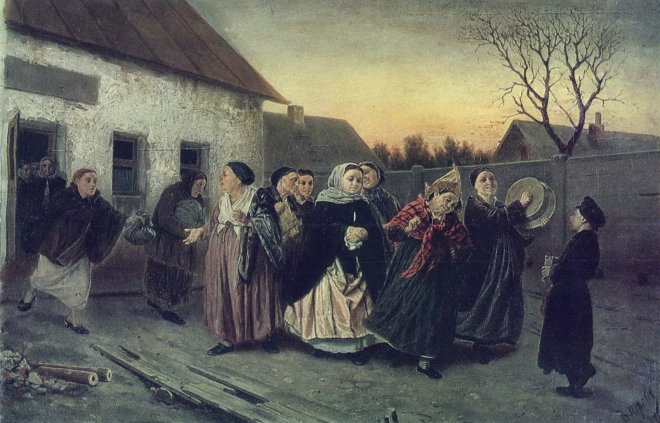
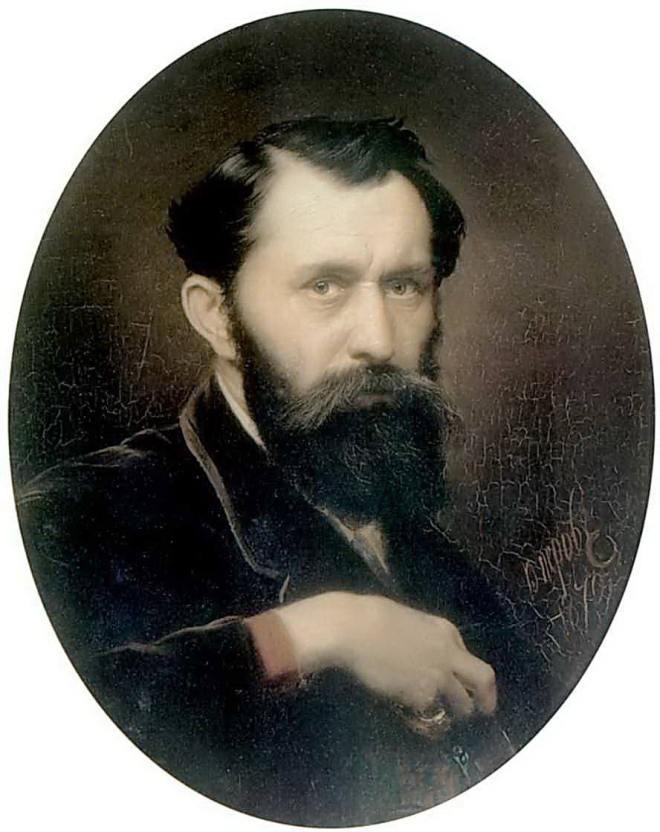
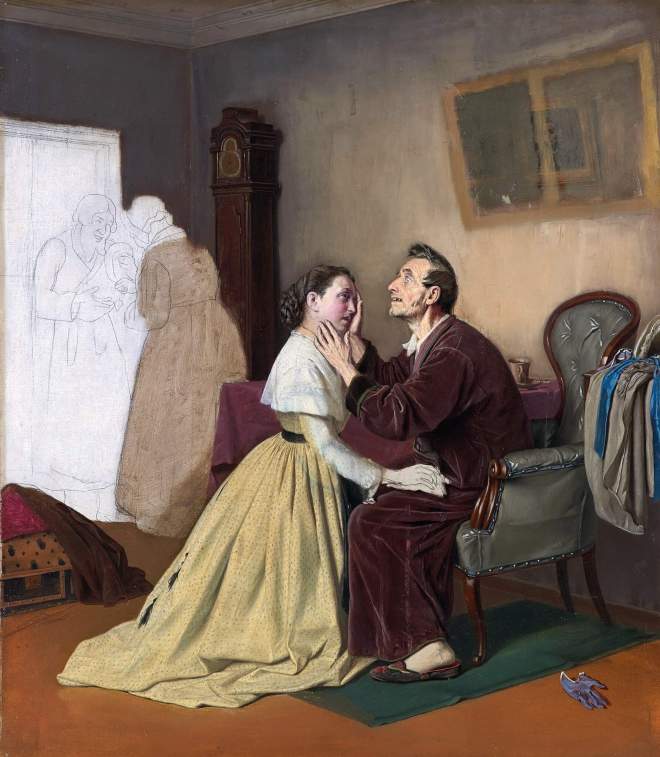
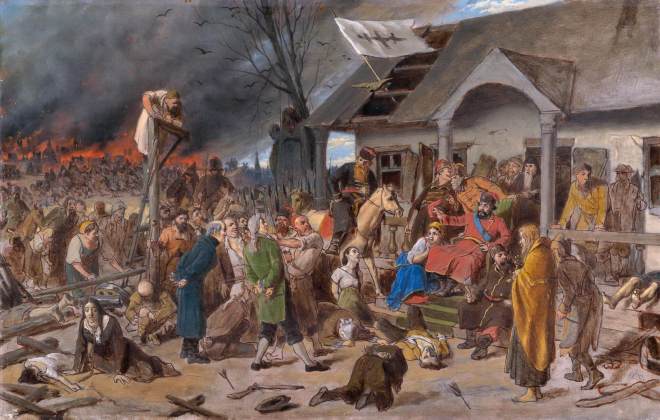
Vasily Perov était un grand artiste russe du XIXe siècle, dont les œuvres ont ouvert de nouveaux horizons à l’art russe. Ses peintures sont profondes et complexes, et démontrent toute la vérité sur la dure vie du peuple. Vasily était aussi un grand professeur qui a élevé plus d’une douzaine de très grands peintres. Regardez toutes ses peintures dans un diaporama et appréciez sa biographie.
Liste des Peintures de Vasily Perov en français dans l’ordre du diaporama
Vasily Grigoryevich Perov est né entre le 21 et le 23 décembre 1833 (2 ou 4 janvier 1834) et est le fils illégitime du baron Georgy (Grigory) Karlovich Kridener et d’AI Ivanova.
Même si ses parents se sont mariés peu de temps après sa naissance, Vasily n’avait pas droit au nom et au titre de son père. Et son surnom “Perov”, qui est son nom de famille, lui a été donné par son professeur de literacy pour sa diligence et son écriture habile.
Dans son enfance, Vasily était malade de la variole, ce qui lui a causé une mauvaise vue pour le reste de sa vie.
Il s’est intéressé à la peinture après avoir observé le travail d’un artiste et est allé étudier à l’école d’art Arzamas d’AV Stupin. Mais parce qu’il était si bon qu’il a été autorisé à peindre avec des peintures à l’huile avant les autres élèves, puis malheureusement à cause d’une dispute avec un autre élève, il n’a pas terminé l’école.
Il est rentré chez lui et a commencé à créer la composition « Crucifixion » écrite tout au long du Carême et achevée la Semaine Sainte puis placée dans une église située près du village de Nikolskoye.
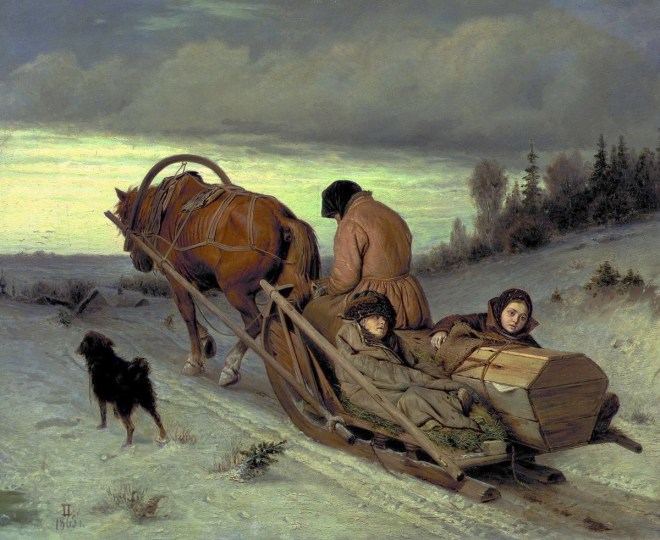
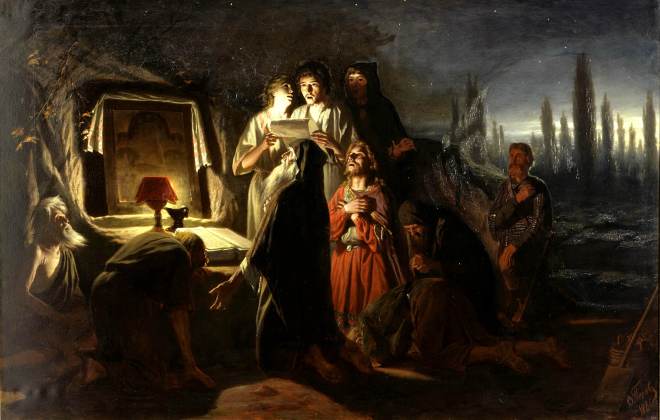
Il a également peint un certain nombre de portraits et de tableaux de genre : « Un mendiant qui mendie », « Troïka du village », « Festival folklorique dans la Semik ».
En 1853, Vasily Perov est entré à l’école de peinture, de sculpture et d’architecture de Moscou et a obtenu son diplôme universitaire sous la direction de SK Zaryanko.
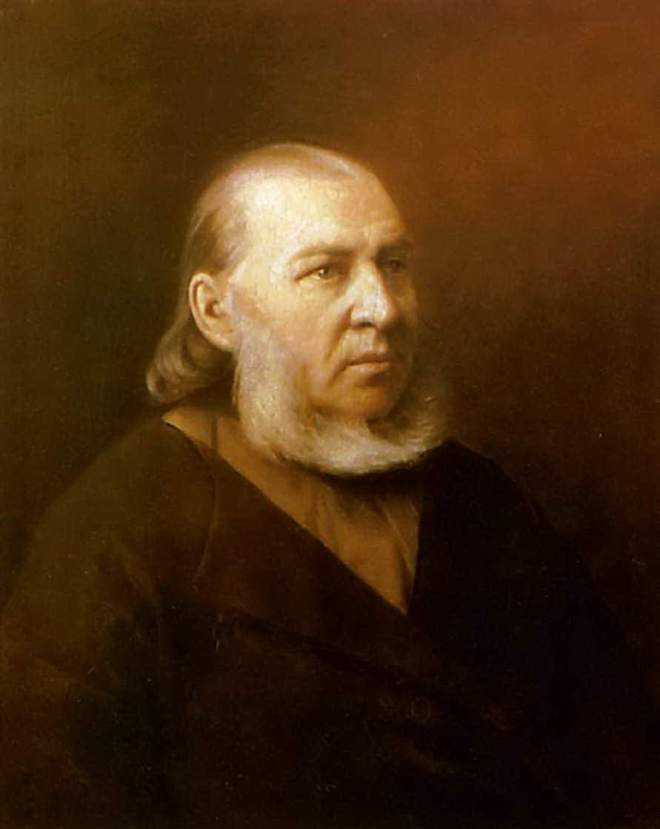
Perov a présenté le “Portrait de Nikolai Grigoryevich Kridener, le frère de l’artiste” à l’Académie impériale des arts et a reçu une petite médaille d’argent en 1856.

Ce travail était encore étroitement lié aux traditions de l’art du début du XIXe siècle, mais déjà dans les travaux suivant, Perov agissait comme un innovateur.
En 1857, le tableau “Arrivée d’un policier pour enquête” rapporte à l’artiste une grande médaille d’argent et attire l’attention du public et des critiques.
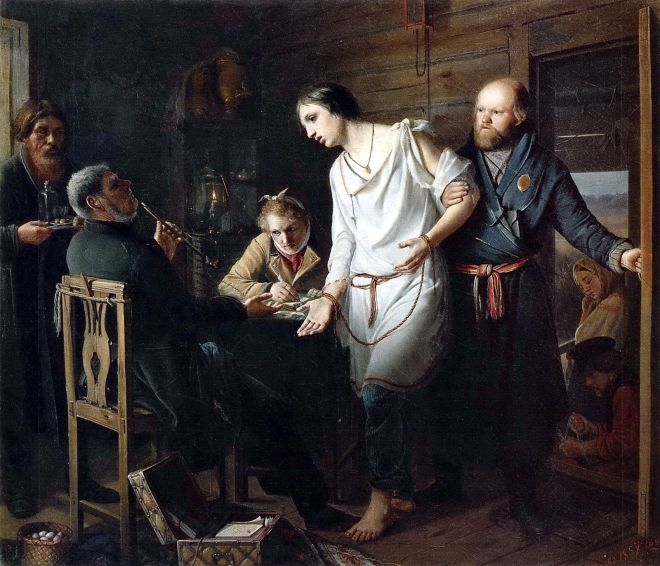

En 1860, Perov reçut à nouveau une petite médaille d’or pour le tableau «Premier rang. fils de sacristain, promu greffier collégial », qui érigea l’artiste en héritier du genre satirique des années 1840.
Maintenant, il pouvait participer au concours pour une grande médaille d’or, et peint “Sermon dans le village” et “Procession religieuse rurale à Pâques”. Il reçu une grande médaille d’or en 1867 et le droit de voyager à l’étranger comme pensionnaire pour le premier tableau.

En 1862, Perov épousa Elena Edmondovna Sheins et ils partirent à l’étranger alors qu’il était lui-même pensionnaire à l’Académie des Arts.
En 1863-1864, Perov a vécu et travaillé à Paris, mais il voulait rentrer chez lui et après avoir reçu l’autorisation de l’Académie pour un retour anticipé qui comprenait la poursuite de l’internat en Russie, il est retourné à Moscou.
Vasily Perov s’est installé dans la maison de l’oncle de sa femme, F.F. Rezanov à Moscou et n’a jamais quitté la ville.
Alors qu’il était encore à l’étranger, Perov a conçu un grand tableau avec une intrigue de la vie monastique, avec ces peintures, une nouvelle étape dans le travail de l’artiste a commencé: d’une direction satirique, il est passé à des histoires plus dramatiques – sur «l’humiliation et l’offense.
En 1869, Vasily Perov et Myasoedov créent l’Association des expositions d’art itinérantes (TPKhV). Vasily, qui a été membre du conseil d’administration pendant 7 ans, a organisé un groupe de Wanderers à Moscou.
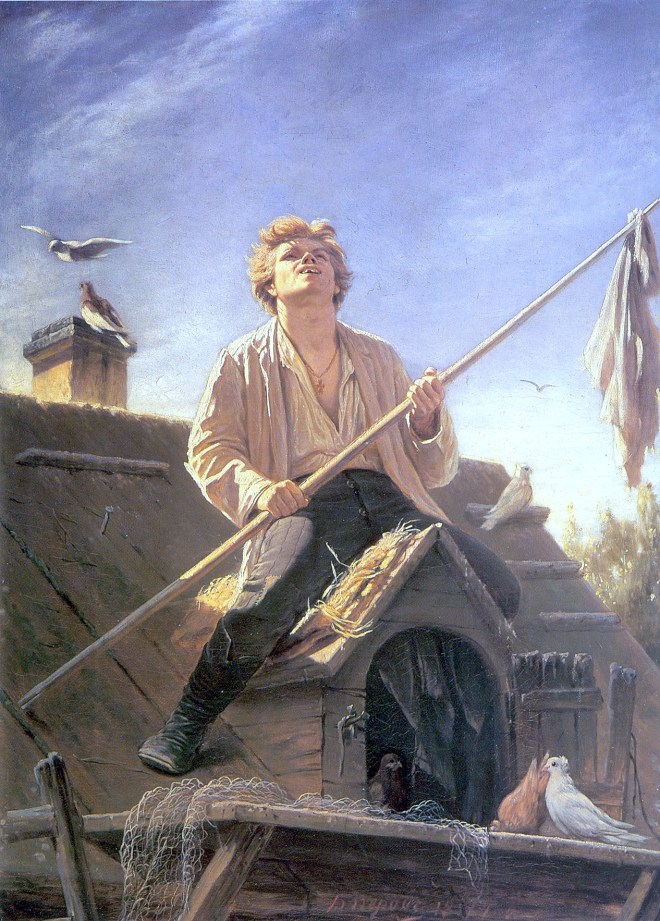
En 1870, il a obtenu le titre de professeur de l’Académie des Arts grâce aux tableaux “Vagabond” et “Attrape-Oiseaux”, et reçoit le premier prix de l’OPH pour le tableau “L’Homme-Oiseau”.

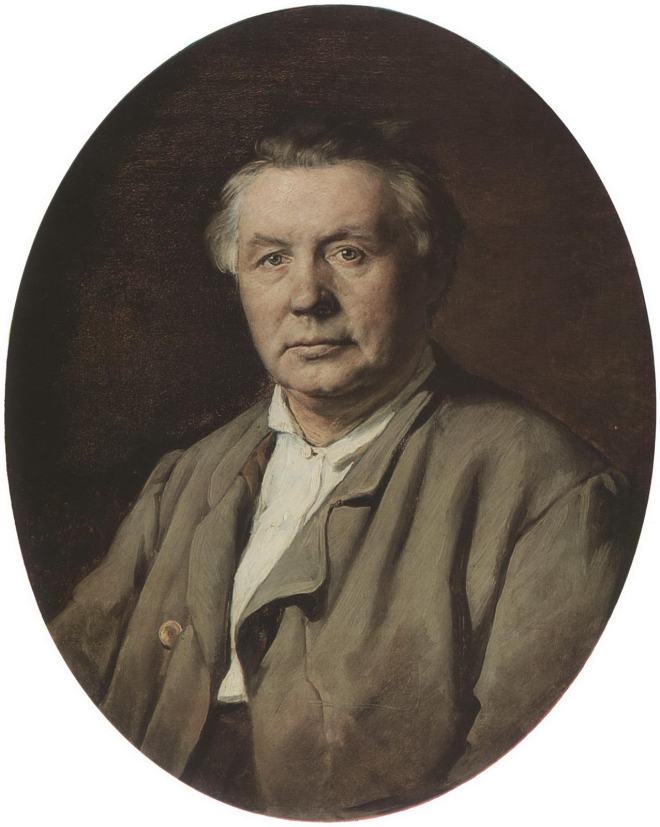
Dans les années 1970, les histoires de la vie quotidienne occupent une place particulière dans l’œuvre de Perov. Puis en 1871, Vasily est nommé professeur à l’École de peinture et d’art de Moscou.
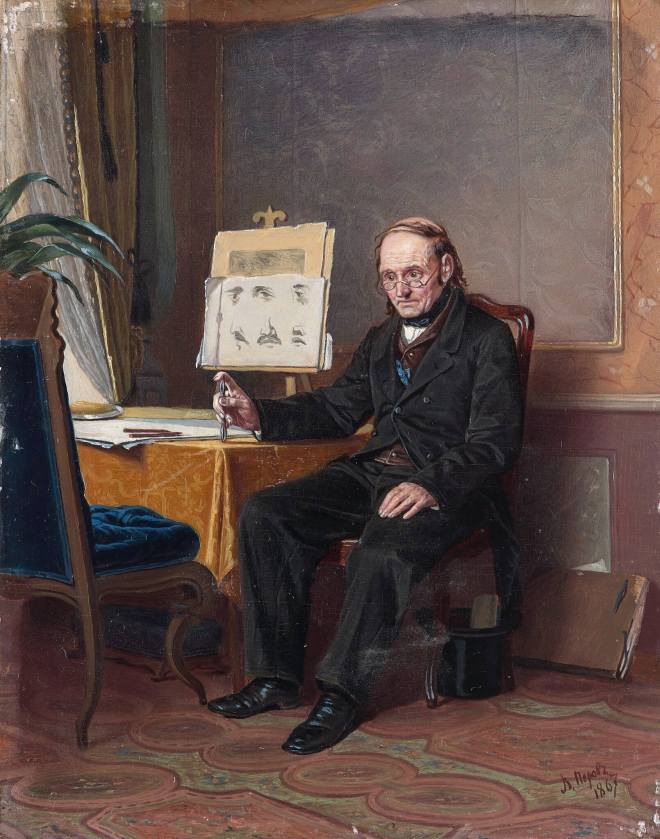
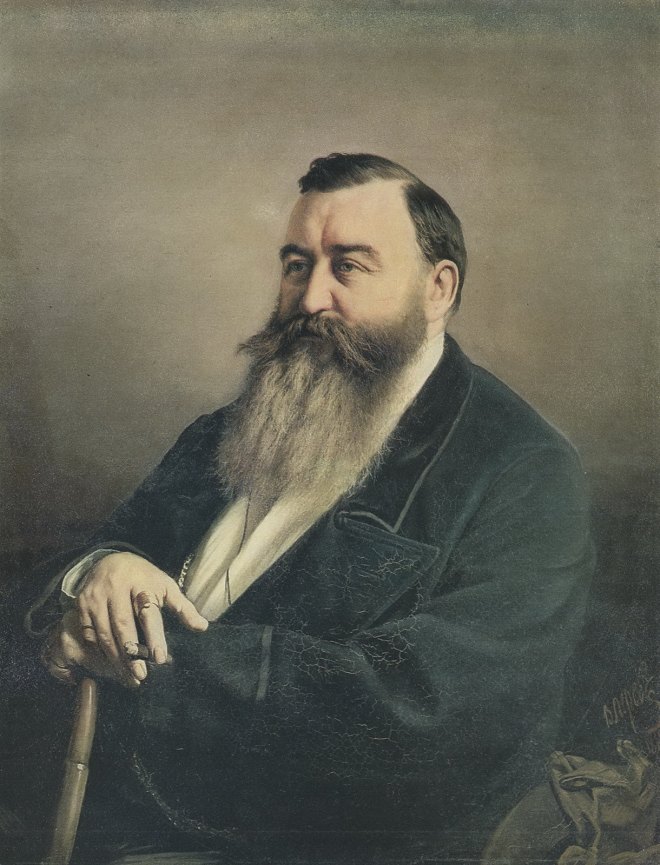
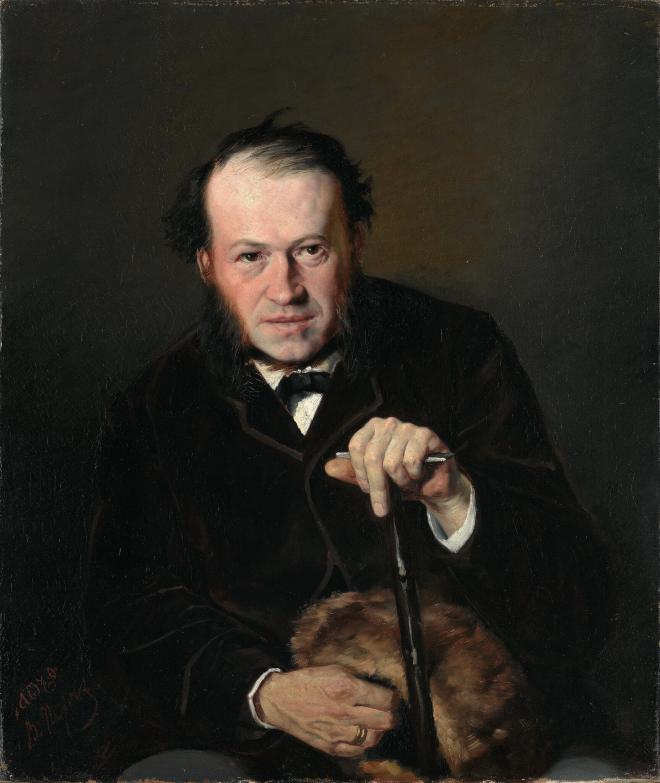
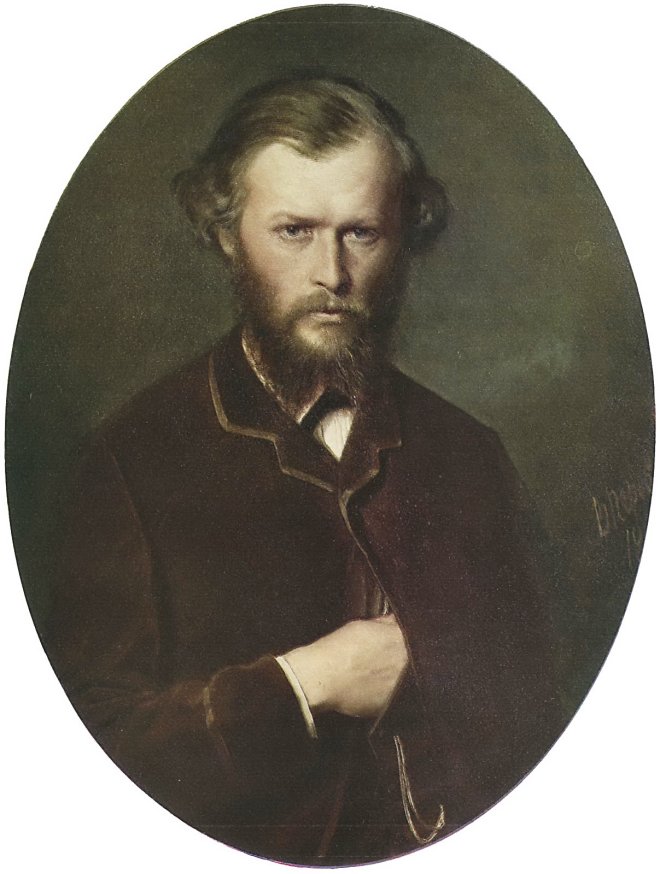
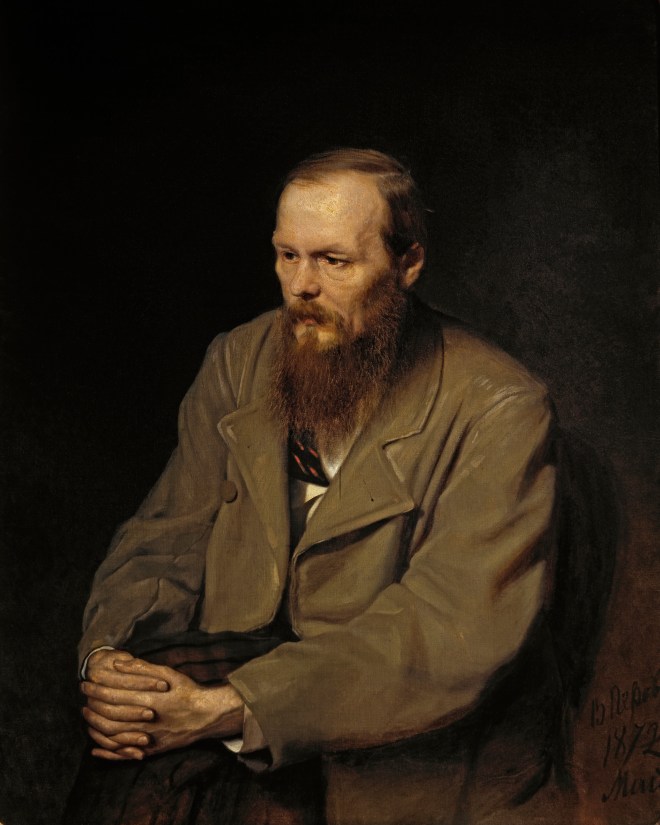
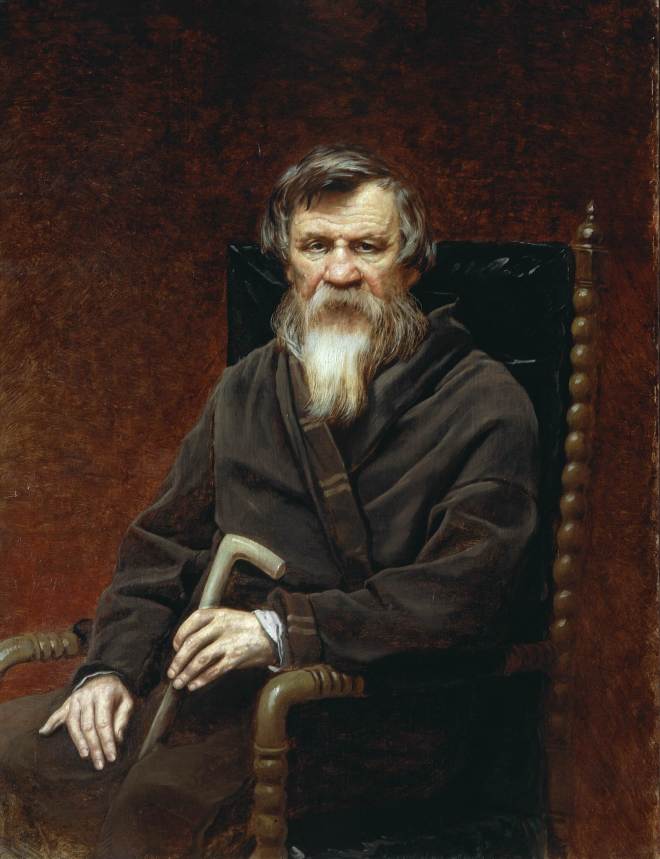
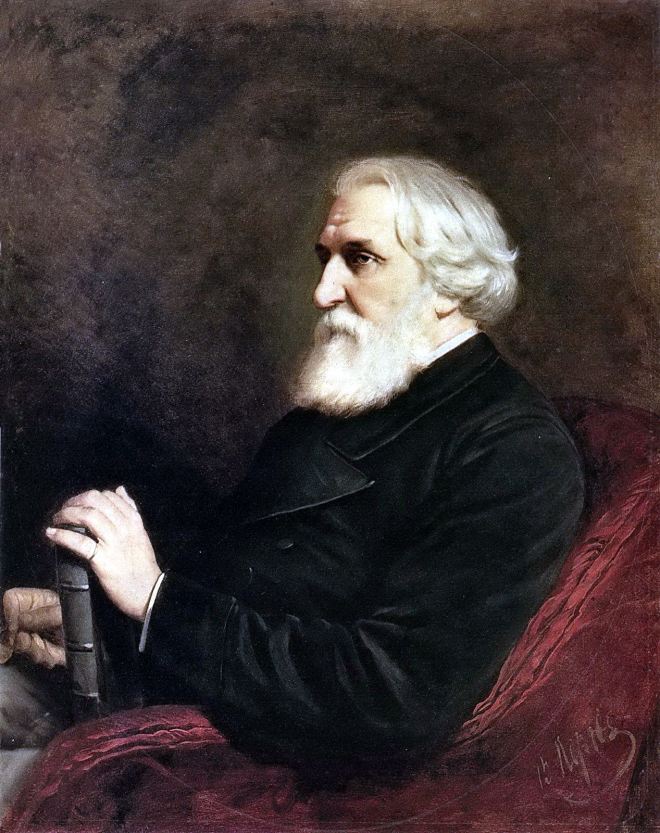
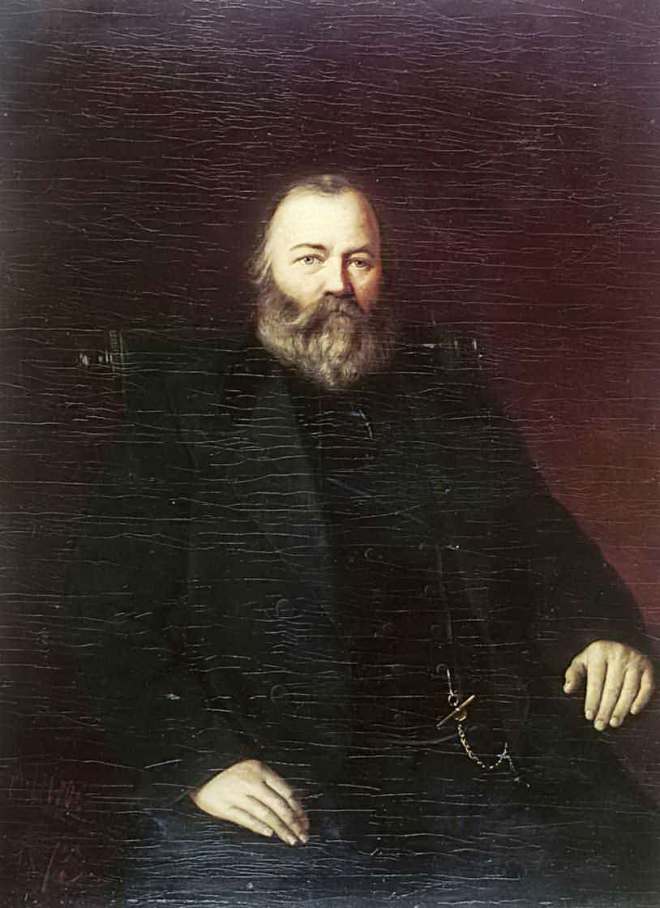
En 1871-1872, Perov, commandé par le Premier ministre Tretiakov, a exécuté un certain nombre de portraits d’écrivains et de scientifiques russes. Perov a atteint une telle «vérité» dans certains portraits, ce qui dans l’art russe n’a été atteint que par IE Repin et VA Serov .
Perov a épousé Elizaveta Egorovna Druganova en 1872.
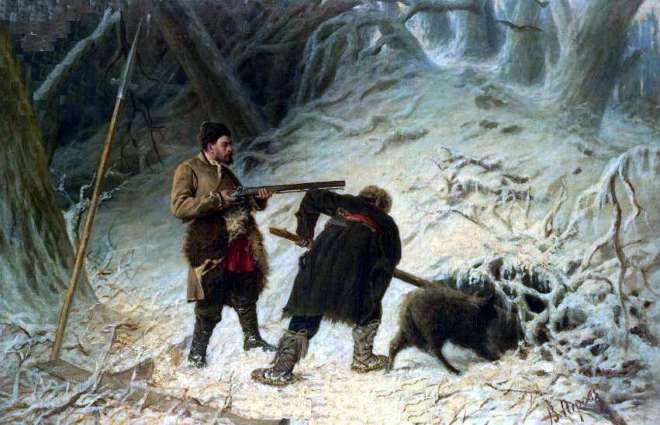
En 1873, ses tableaux “Pêcheur” et “Chasseurs au repos” sont présentés à l’Exposition universelle de Vienne.

En 1877, Perov a quitté les membres du TPHV et a participé à l’exposition de l’Exposition universelle de Paris un an plus tard.
Au cours des dernières années de sa vie, VG Perov a collaboré avec la revue ” Priroda i Okhota ” de LP Sabaneev et un certain nombre de ses histoires ont été publiées dans le Art Journal qui a été publié en 1881-1887.
Sa santé se détériora à cause du typhus et d’une pneumonie en 1881 et Vasily Perov mourut de consomption, à l’âge de 49 ans, dans un petit hôpital de Golitsyn près de Moscou.
Perov a été enterré au cimetière du monastère, du monastère de Danilov où une pierre tombale lugubre en forme de croix sur le Golgotha a été érigée sur sa tombe.
Plus tard, ses cendres ont été réenterrées au cimetière du monastère du monastère de Donskoy, et sur la nouvelle tombe de l’artiste, un monument a été érigé par le sculpteur Alexei Evgenievich Yeletsky.
J’espère que cet article vous a plu
Lisez l’article: Découvrez le tableau “Troïka” de Vasily Perov
| Si vous avez aimé cet article, abonnez-vous, mettez des likes, écrivez des commentaires ! |
Partager sur les réseaux sociaux |
Découvrez nos derniers posts |